English
English
Jabra Sanitary is a sanitaryware supplier offering toilets, sinks, faucets, bathtubs, etc., at competitive prices. If you're a distributor, wholesaler, or project contractor, get a quote today!
 $23.9 Limited-time Offer
$23.9 Limited-time Offer Consignment Policy
Consignment Policy 20 Years of Experience
20 Years of Experience
Toilets are essential to modern life. Have you ever wondered how toilets are made?
Making toilets involves combining traditional ceramic techniques and modern manufacturing technologies.
This guide will take you through each step of toilet manufacturing—from selecting raw materials to the final shipping—shedding light on the detailed processes behind toilet making.
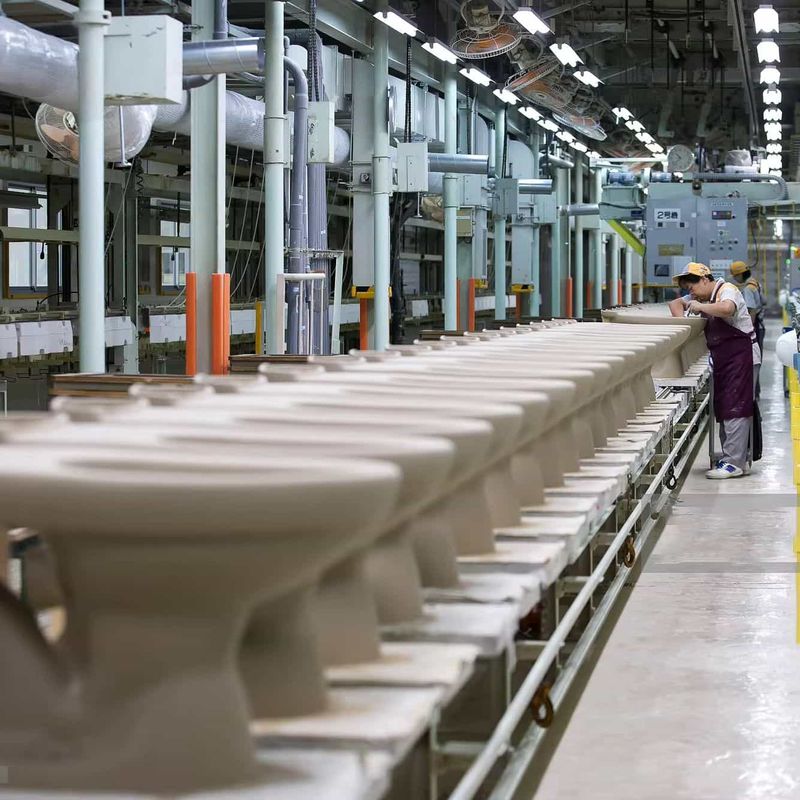

Table of Contents
Materials Used
Design and Modeling
How Toilets Are Made?
Toilet Assembly and Installation Components
Why are Toilets Made of Ceramic?
Environmental Consideration
Innovations and Technology
Choosing the Best Flushing Toilet
Conclusion
Materials Used
The primary material used in toilets is ceramic, most commonly porcelain.
Porcelain is favored for its durability, moisture resistance, and ability to be easily molded.
They can be applied to create smooth and watertight surfaces, perfect for sanitary ware.
- Clay: The main ingredient of porcelain is clay, especially kaolin, combined with minerals like feldspar and quartz.
- Water: Water is used throughout the process to mix materials and to help shape the clay.
- Glaze: A ceramic glaze is applied to the surface to create a glossy finish that is also water-resistant.
These ingredients are carefully filtered to remove any impurities before being thickened and stored, ready for casting.
In addition, various metals and plastics can be used for the flushing mechanism and the toilet seat.
Many toilet manufacturers are adopting more sustainable practices. They select materials not only for their functionality but also for their environmental impact.

Next, we will discuss the design and modeling stage, where the initial concepts for toilets take shape before moving into production.
Design and Modeling
The design of a toilet is crucial as it impacts not only aesthetics but also ergonomics and water efficiency.
The process starts with toilet sketches, usually made by industrial designers who focus on functionality and user experience.
Concept Development: Designers will consider various factors like size, shape, and style.
They must ensure that it meets both consumer preferences and regulatory standards for water usage.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): After sketching, the designs are transferred into CAD software. This allows designers to create detailed 3D models of the toilets, which can be tested and modified digitally.
CAD models provide a precise visualization of the final product and facilitate the creation of the molds used in the manufacturing process.
How Toilets Are Made?
Below, let's delve into the ceramic toilet manufacturing process, from raw materials to the finished product.
Step 1: Prepare Raw Material
The process starts with the preparation of raw materials. High-quality clay, along with other components, is carefully selected and blended to form the ceramic slip, which is the base for all ceramic products.
Step 2: Stirring The Clay
The clay mixture is thoroughly stirred to ensure a smooth, consistent texture. This step is critical as it affects the quality and integrity of the ceramic, ensuring there are no air pockets or lumps.
Step 3: Molding
The clay slip is then poured into plaster molds. These molds set the initial shape of the toilet. The plaster absorbs excess water from the clay, helping it to solidify without shrinking away from the mold.
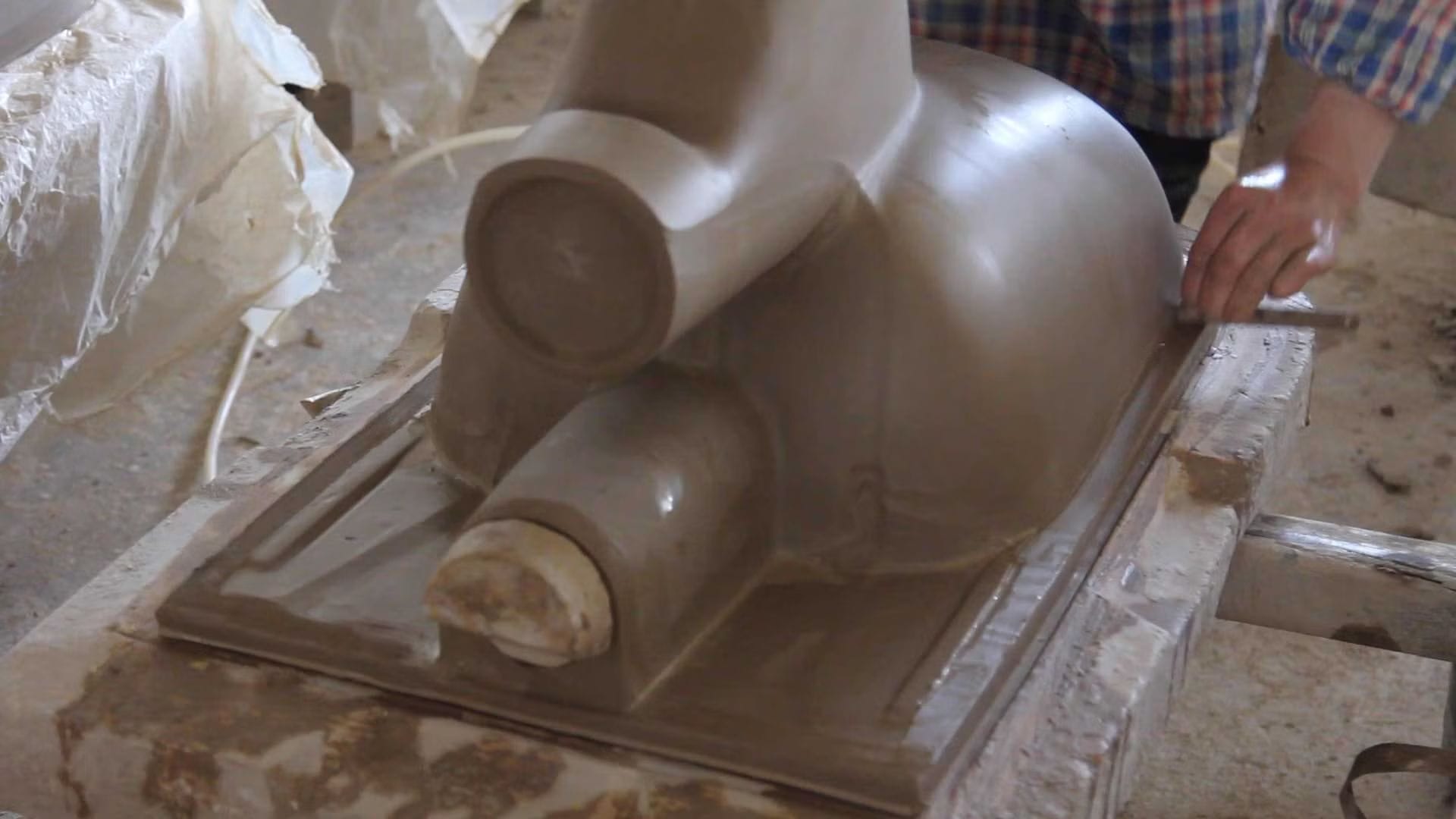

Modern toilet manufacturing often employs high-pressure casting, which quickens the production process, ensures higher quality, and is less affected by weather conditions.
Step 4: Demolding
Once the clay hardens, the molds are carefully removed, revealing the toilet form. This step requires precision to ensure the form is not damaged during the demolding process.
Step 5: Trimming
After the greenware has dried sufficiently, it is trimmed and smoothed. Workers remove any imperfections and refine the shape to meet design specifications, ensuring a high-quality finish.
Step 6: Drying
The items are dried to remove excess moisture and further solidify their structure. Proper drying is crucial to prevent cracks and deformities during the subsequent firing process.
Step 7: Checking and Sanding
Inspect the body for damage. If found, mark for repair; if not, proceed with sanding. Careful sanding ensures the surface is smooth and ready for glazing.
Step 8: Glaze Spraying
The surface is glazed 3-5 times for a smooth glossy finish. Silver ions provide antibacterial properties after sintering, enhancing both the appearance and hygiene of the final product.
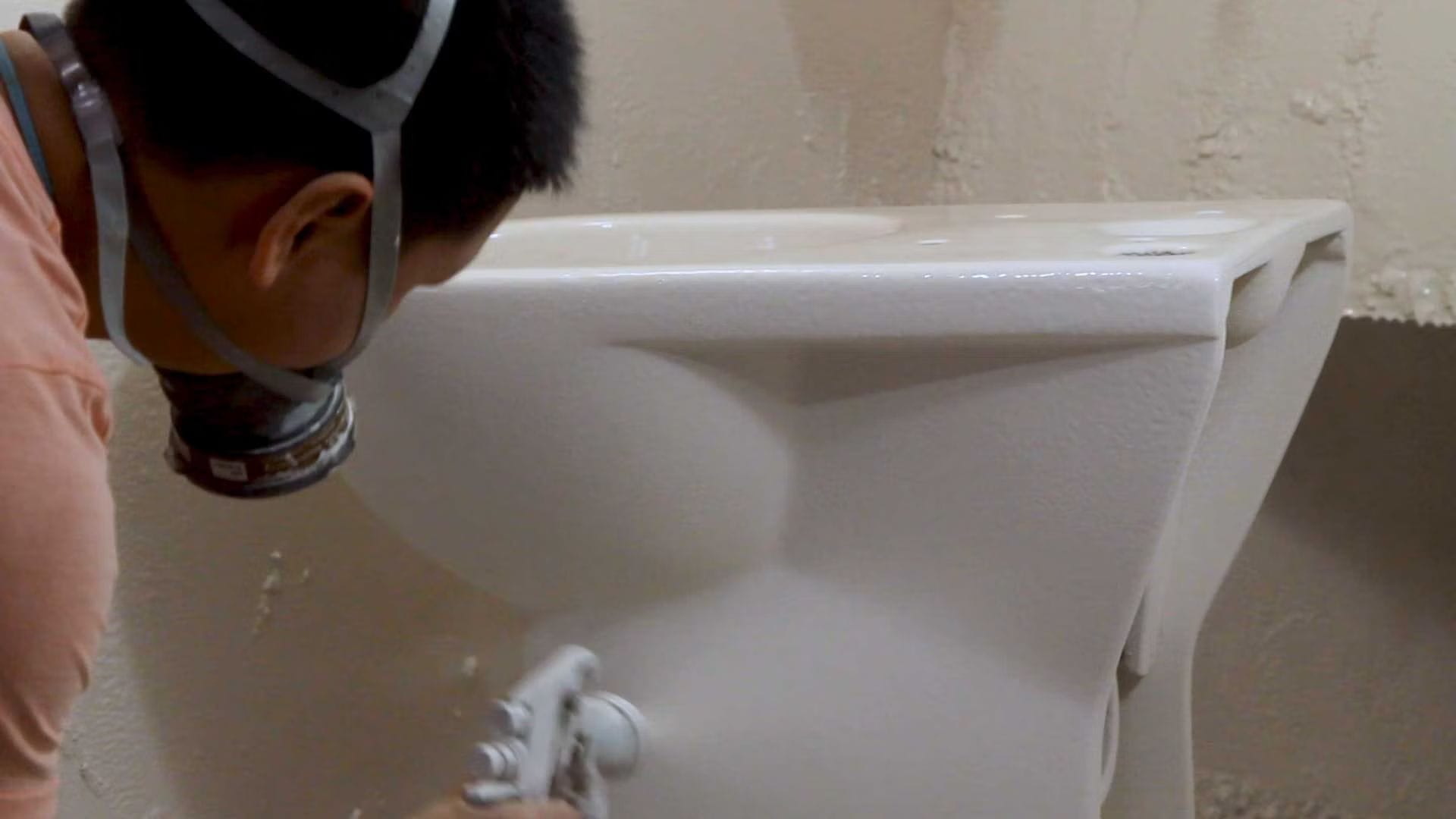

Step 9: Firing in Kilns
The glazed and dried toilets are then fired in a kiln for approximately 40 hours. The kilns' temperature gradually increases to over 1280℃.
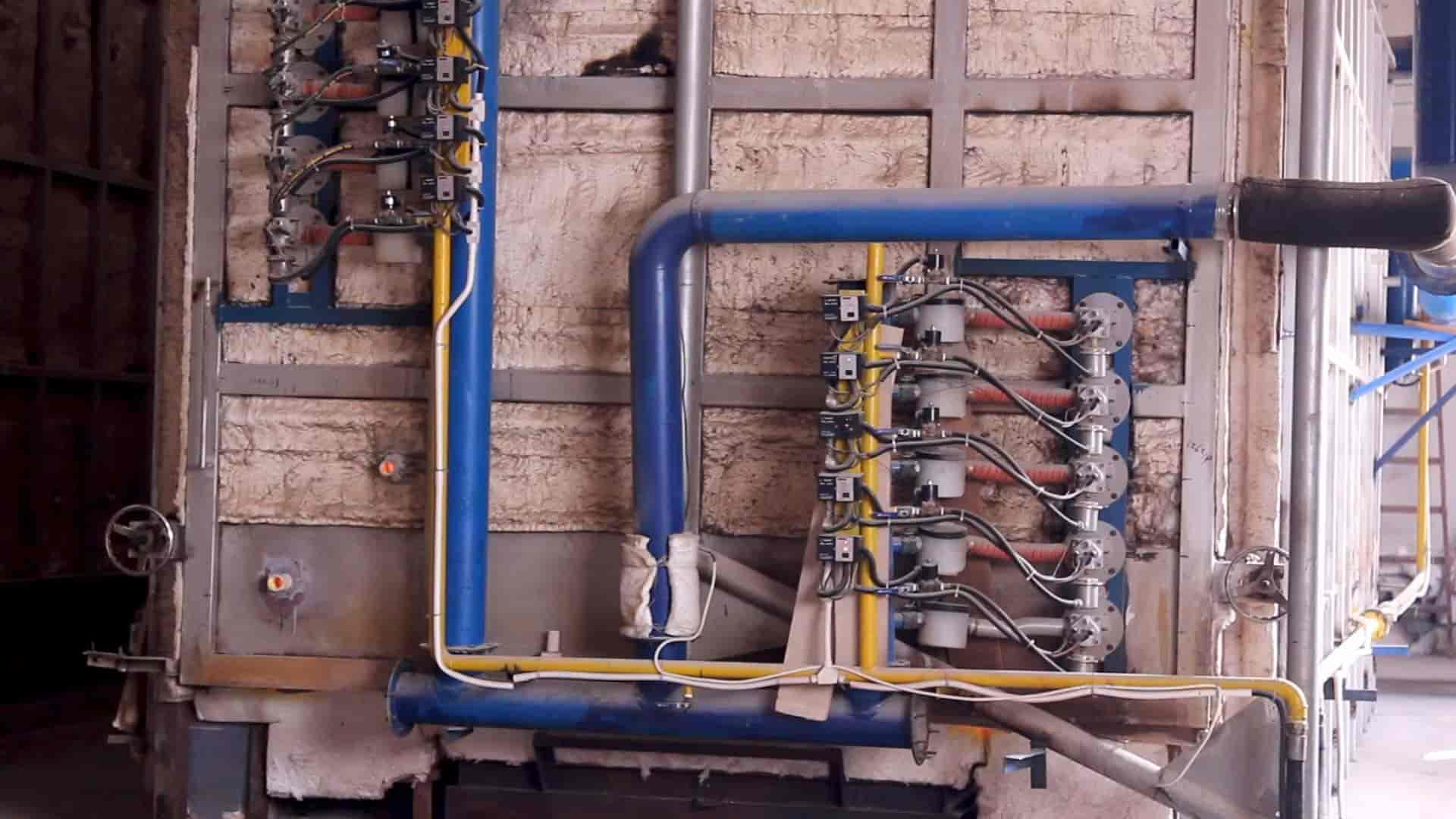
The firing process vitrifies the porcelain, making it strong and durable. This process makes the entire toilet waterproof and stain-resistant.
Step 10: Final Testing
Each toilet undergoes rigorous testing and inspection after firing. Only quality-approved toilets proceed to the packaging stage.
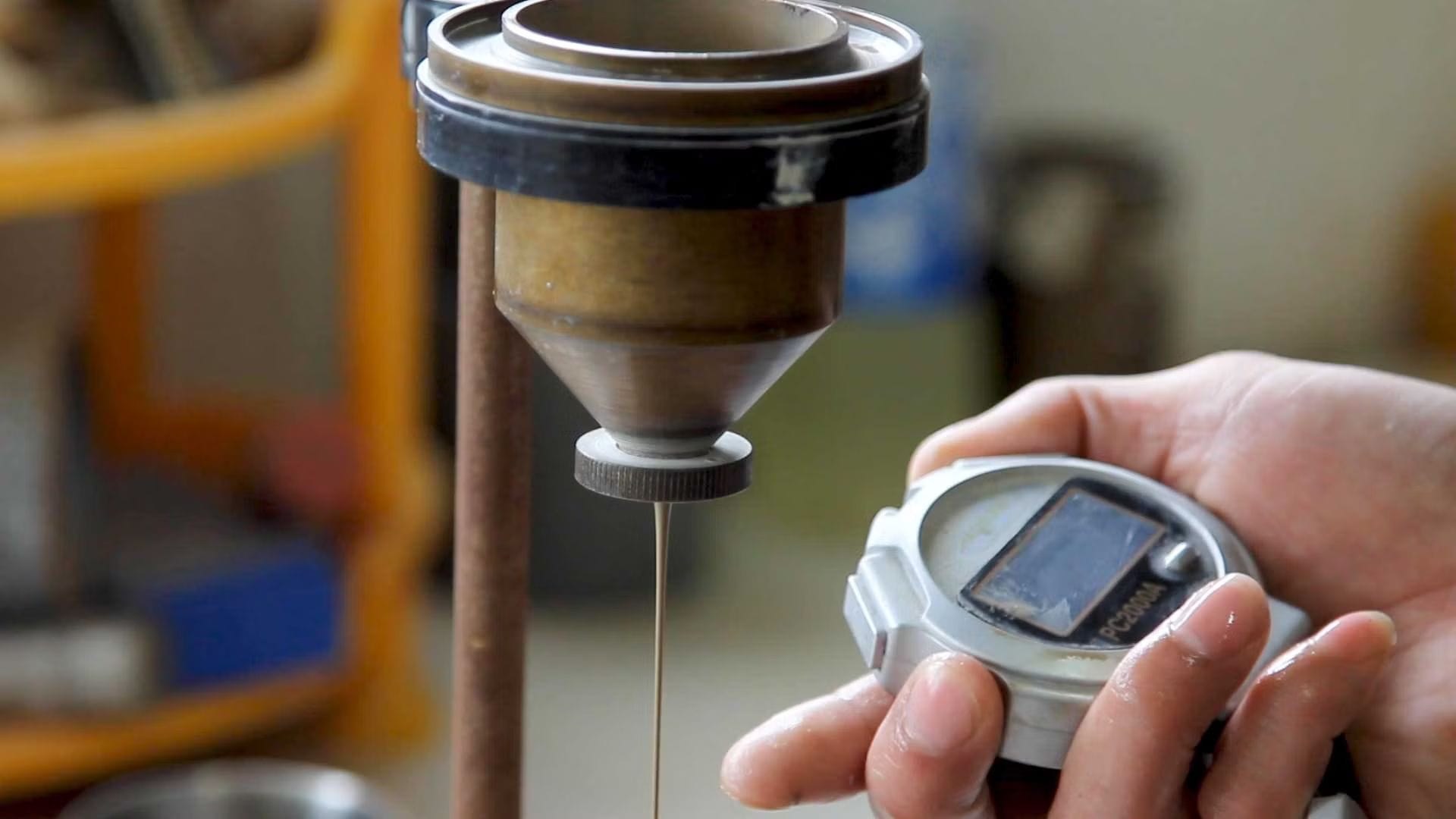

Quality control is paramount in toilet manufacturing, ensuring each product is both durable and reliable. The process includes several tests:
- Surface Quality: Check that the surface is smooth.
- Cracks: Inspect the toilet for any cracks, as they can weaken the structure and durability.
- Structural Integrity: Ensure the toilet maintains its strength and stability.
- Flushing Tests: Conduct flushing tests to ensure efficient waste removal and prevent clogs.
- Water Absorption: Measure the material's water absorption to maintain strength.
- Leak Testing: Each toilet is tested for leaks in its tank and bowl to prevent water wastage.
- Chemical Resistance: Test the toilet's resistance to cleaning agents and other chemicals.
- Resistance to Staining and Burning: Ensure the toilet resists staining and burning to stay clean and safe.
- Strength Testing: Toilets must withstand significant weight and usage over time, so strength tests are conducted to ensure they do not crack or break under pressure
- Compliance with Standards: Toilets must meet specific standards set by regulatory bodies. These standards ensure toilets are safe, efficient, and environmentally friendly.
Step 11: Packaging
Once tested, the toilets are labeled, and packaged with protective materials to prevent damage during transportation. They are moved to a warehouse or distribution center, ready for dispatch.
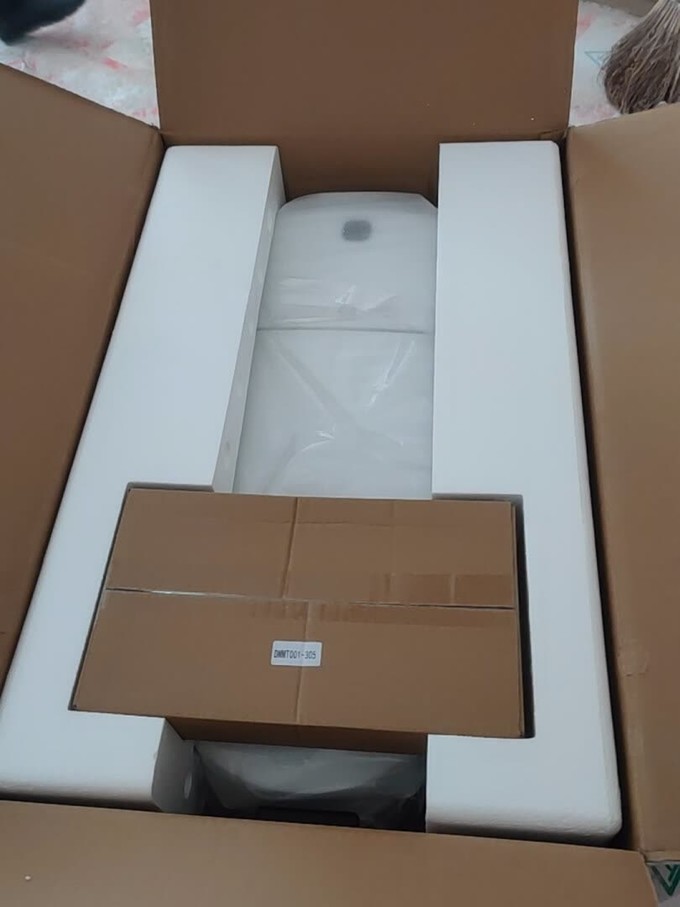

Step 12: Shipping
Finally, the packaged toilets are shipped to toilet retailers and toilet distributors, ready for installation in homes and businesses worldwide.
Toilet Assembly and Installation Components
The assembly of toilets involves several key components:
- Tank Fittings: The flushing mechanism, including the handle, flush valve, and fill valve, is assembled within the tank.
- Seat Installation: The seat and lid are attached using hinges and bolts that allow for easy operation and cleaning.
- Installation Process: Briefly, the installation of a toilet involves securing the bowl to the bathroom floor, connecting the water supply to the tank, and ensuring the waste outlet is properly sealed to prevent leaks and odors.

Ceramic, the primary material for toilets, is a blend of several types of clay, silica, and a fluxing agent. There are three main reasons for its popularity:
- Aesthetics and Durability: Ceramic has a smooth surface, is hard, pressure-resistant, and does not stain easily. It has a high density and low water absorption rate, making it perfect for sanitary ware.
- Ease of Manufacturing: The process of making a toilet, including clay preparation, forming, and porcelain firing, is relatively simple and cost-effective.
- Hygiene: The glazed surface of ceramic toilets makes them easy to clean, highly resistant to bacteria, and helps reduce the spread of diseases.
Other materials such as wood, stone, and plastic have been experimented with over the years, but none have matched the efficiency and practicality of ceramic.
Environmental Consideration
While ceramic toilets have many advantages, they also produce waste during manufacturing. However, much of the clay used in the process is recyclable. As long as the clay hasn't been fired, it can be scrapped, softened, and reprocessed.
Innovations and Technology
Recent advancements in toilet technology focus on enhancing user convenience and environmental sustainability:
Water Efficiency: Modern toilets often feature dual flush technology, which allows the user to choose between a full or reduced flush, significantly lowering water usage.
Smart Toilets: These bidet toilets include features like self-cleaning technologies, seat warmers, and automated flush systems, which enhance comfort and bathroom hygiene.
Eco-Friendly Materials: Manufacturers are increasingly using recycled materials and developing new types of ceramics and plastics that reduce environmental impact during production and disposal.
Use Renewable Resources: We put solar panels on the rooftop of our factory to provide energy-efficient power and reduce reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
These innovations improve the functionality and user experience of toilets and contribute to broader environmental conservation efforts.
Choosing the Best Flushing Toilet
When buying a ceramic toilet, consider weight (heavier toilets often indicate better quality), water fittings, glaze material, discharge caliber, and flushing method.
The right toilet can significantly enhance bathroom aesthetics and functionality.

When buying a toilet, consider weight (heavier toilets often indicate better quality), water fittings, glaze material, discharge caliber, and flushing method. The right toilet can significantly enhance bathroom aesthetics and functionality.
Manufacturing toilets is a blend of art, science, and engineering. As we continue to innovate and improve sanitary solutions, it's interesting to reflect on the complex process that creates this everyday essential.
Conclusion
The manufacturing of toilets combines artistry and engineering, requiring precise control over materials and processes.
Each step, from raw material preparation to shipping, is crucial in ensuring the final product meets the expected standards of functionality and quality.
Innovations in design and materials continue to improve the efficiency and sustainability of toilets, reflecting the evolving demands of modern society.
The journey of crafting a toilet is a testament to our relentless pursuit of improving sanitation and hygiene. The next time you use a toilet, take a moment to appreciate the artistry, engineering, and history behind it.